Analysis of a Motor Control Circuit supplied by a
Control Transformer using Section 430.72
Control Transformer Protection Problems:
Problem No. 1:
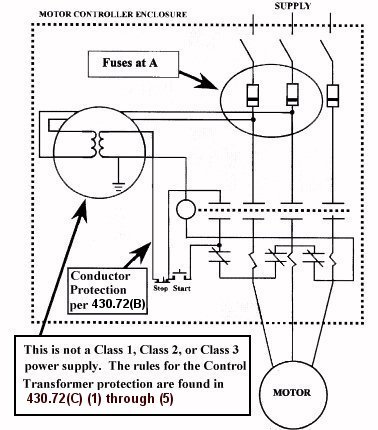
(Use Figure 1)Assuming that the motor controller control circuit requires 300 VA 120/480 volt control transformer for a 480 volt controller, using the 500 per cent rule determine the maximum size motor power circuit fuses that would be allowed at "A" for protecting a 350 VA control transformer.
The basic rule is to protect the control transformer using the rules for transformers in Article 430.72(C)(1), (2), (3), (4), or (5).
(1) Requires control transformers with a rated primary current less than 2 amperes to be protected by an overcurrent device set at not more than 500 per cent of the rated primary current.
(2) Allows protection of transformers to comply with Section 450.3, the general transformer protection section.
(3) Requires control transformers rated smaller than 50 VA located in the motor controller to be protected by primary overcurrent devices, impedance limiting means, or other inherent protection means.
(4) States that where the control circuit transformer rated primary current is less than 2 amperes and the overcurrent device is rated or set at not more than 500 per cent of the rated primary current of the transformer then the primary overcurrent device is permitted to protect the control transformer.
(5) Permits protection by other approved means. This means the authority having jurisdiction can accept other approved means of protection.
An Exception to 430.72(c) eliminates the requirements for
protection where opening the control circuit presents a hazard such as controls
for fire pumps.
Solution:
Primary current = 350VA/480 volts
Primary current = .73 amperes.
500 % of .73 amperes = 3.6 amperes.
The maximum size fuses at "A" would be 3.6 amperes.
Problem No. 2
(Use Figure 1):(a) Using the 500 per cent rule what is the maximum size fuses at "A" and maximum size control transformer that can be used for a 120/208 volt control transformer?
(b) For a 3-phase 208 volt induction motor what is the maximum horsepower that this control circuit can be used for if the primary overcurrent device is an inverse time circuit breaker?
Solution:
(a) Maximum primary current for the transformer is less than (<) 2 amperes
at 208 volts per 430.72(C)(1)
Maximum size transformer is 2 x 208 volts < 416 VA.
Maximum size fuses at "A" < 500 per cent x 2 amperes or
Maximum size fuses at "A" shall be less than 10
amperes.
(b) At 208 volt, 3-Phase, and with a less than 10 ampere inverse
time CB, 2.5 FLA < 10. Then FLA would be 10/2.5. FLA
< 4 amperes.
The maximum Horsepower from Table 430.150 for a FLA of less than 4 amperes
and 3-phase voltage of 208 volts is 3/4 Hp with a FLA of 3.5 amperes.
(round down.)
Protection of the Control Circuit Conductors supplied by a Control Transformer.
Problem No. 3:
(Use Figure 1)Given: A motor control circuit requires a 125 Volt-Ampere 208 volt to 24 volt control transformer. What is the maximum size fuses that can be installed at "A" for this circuit if the control circuit conductors do not exit the controller enclosure? Find the maximum fuses for No. 18, No. 16, No. 14, No. 12, and No. 6 copper conductors.
The general rule for protecting tapped Motor Control Circuit conductors is to use Table 430.72(b).
However there are 2 exceptions to these rules. Exception No. 2 applies to conductors supplied by the secondary side of a single phase transformer. This rule states:
"Conductors supplied by the secondary side of a single-phase transformer having only a two-wire (single-voltage) secondary shall be permitted to be protected by overcurrent protection provided on the primary (supply) side of the transformer, provided this protection does not exceed the value determined by multiplying the appropriate maximum rating of the overcurrent device for the secondary conductor from Table 430.72(b) by the secondary-to-primary voltage ratio."
Mathematically this statement converts to the following:
Primary Protection (PP) <= Secondary Voltage/ Primary Voltage) x (Maximum
rating of overcurrent device for conductor from table 430 72(b))
Solution:
PP <= (24/208) x (25 amperes from Column B of Table 430.72(b) for No.
18 copper)
PP<= 2.8 amperes
PP<=(24/208) x ( 40 amperes for No. 16)
PP<= 4.6 amperes
* PP<=(24/208) x (100 amperes for
No. 14)
* PP<= 11.5 amperes
* PP<=(24/208) x (120 amperes for No.
12)
* PP<= 13.8 amperes
* PP<=(24/208) x (80 amperes from Table
310.17 x 400 per cent per Note 2 to Table 430.72(b))
* PP<= 36.9 amperes
Problem No. 4:
Solve the same problem for Motor circuit conductors that exit the motor controller using Column C of Table 430.72(b)PP <= (24/208) x (7 amperes from Column C of Table 430.72(b)
for No. 18 copper)
PP<= .8 amperes
PP<=(24/208) x ( 10 amperes for No. 16)
PP<= 1.2 amperes
PP<=(24/208) x (45 amperes for No. 14)
PP<= 5.2 amperes
PP<=(24/208) x (60 amperes for No. 12)
PP<= 6.9 amperes
PP<=(24/208) x (55 amperes from Table 310.16 x 300 per cent per Note 3
to Table 43 0.72(b))
* PP<= 19.0 amperes
* Although these values satisfy the
protection requirements for the conductors, these solutions can not be used
as shown in the diagram because the control transformer cannot be protected
by the motor short circuit and ground fault protective device unless it has
a value below 10 amperes.